
Comparing with other methods
BigOmics Analytics
Source:vignettes/compare-methods.Rmd
compare-methods.RmdFast pre-ranked enrichment methods
For comparisons, we selected some of the currently fastest pre-ranked gene set enrichment algorithms:
fGSEA (fast GSEA). fGSEA is currently perhaps the most widely used algorithm for pre-ranked enrichment testing. See: github bioRxiv
cameraPR (pre-ranked Camera from the limma package). A version of the Camera method for pre-ranked lists. See: paper
GOAT (Gene set Ordinal Association Test). A very fast method using precomputed null distributions. See: paper github.
In particular we are interested as how we compare to these algorithms in terms of runtime, score and p-value.
Preparing the sparse gene set matrix
For this benchmark we use the example dataset from the
fgsea package which includes some examples gene sets
examplePathways (1457 sets) and an example ranked list
exampleRanks (12000 genes). We filter out gene sets with
less than 10 genes, partly because GOAT cannot handle these. After
filtering, we retain 761 gene sets.
library(fgsea)
library(goat)
#> Loading required package: dplyr
#>
#> Attaching package: 'dplyr'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter, lag
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
library(ultragsea)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'ultragsea'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:fgsea':
#>
#> fgsea
data(examplePathways)
data(exampleRanks)
fc = exampleRanks
gmt = examplePathways
range(sapply(gmt,length))
#> [1] 1 2366
gmt <- lapply(gmt, function(s) intersect(s,names(fc)))
gmt <- gmt[sapply(gmt,length)>=10]
G <- gmt2mat(gmt)
length(fc)
#> [1] 12000
length(gmt)
#> [1] 761Running the methods
Run the code below if you want to increase the number of gene sets for testing.
if(0) {
## run this to increase the number of gene sets.
gmt <- rep(gmt,40)
length(gmt)
names(gmt) <- make.unique(names(gmt))
G <- do.call(cbind, rep(list(G),40))
colnames(G) <- make.unique(colnames(G))
dim(G)
}For benchmarking, we use peakRAM to measure runtime and memory usage of each method.
library(peakRAM)
gs <- names(gmt)
tt <- peakRAM::peakRAM(
res.fgsea <- fgsea::fgsea(gmt, fc, eps=0),
res.cameraPR <- limma::cameraPR(fc, gmt, use.ranks=FALSE)[gs,],
res.ultragsea.z <- ultragsea(G, fc, method='ztest')[gs,],
res.ultragsea.c <- ultragsea(G, fc, method='cor')[gs,],
res.cortest <- gset.cortest(G, fc, compute.p=TRUE, use.rank=FALSE),
res.ztest <- gset.ztest(G, fc),
res.goat <- goat(gmt, fc, filter=FALSE)
)
tt[,1] <- gsub("res[.]|<-.*","",tt[,1])
kableExtra::kable(tt)| Function_Call | Elapsed_Time_sec | Total_RAM_Used_MiB | Peak_RAM_Used_MiB |
|---|---|---|---|
| fgsea | 4.335 | 1.3 | 43.8 |
| cameraPR | 0.317 | 0.8 | 42.4 |
| ultragsea.z | 0.026 | 0.1 | 5.8 |
| ultragsea.c | 0.037 | 0.9 | 9.5 |
| cortest | 0.004 | 0.1 | 2.8 |
| ztest | 0.005 | 0.0 | 2.8 |
| goat | 0.244 | 4.4 | 23.7 |
rt <- tt[,2]
names(rt) <- tt[,1]
par(mar=c(5,8,2,2))
barplot(sort(rt,decreasing=TRUE), horiz=TRUE, las=1, log="x",
xlab="runtime (sec)")
Comparing the scores
We can compare the scores between the methods. We see that all scores
are very correlated to each other. CameraPR does not return a score
value, so for the score we computed -log(p)*sign as its
score. Before plotting we need to make sure all results tables are
aligned.
res.fgsea <- res.fgsea[match(gs,res.fgsea$pathway),]
res.goat <- res.goat[match(gs,res.goat$pathway),]
res.cameraPR$score <- -log(res.cameraPR$PValue)*(-1+2*(res.cameraPR$Direction=="Up"))
Z <- cbind(
fgsea = res.fgsea$NES,
cameraPR = res.cameraPR$score,
ultragsea.z = res.ultragsea.z$score,
ultragsea.c = res.ultragsea.c$score,
goat = res.goat$score
)
pairs(Z, pch='.',cex=4)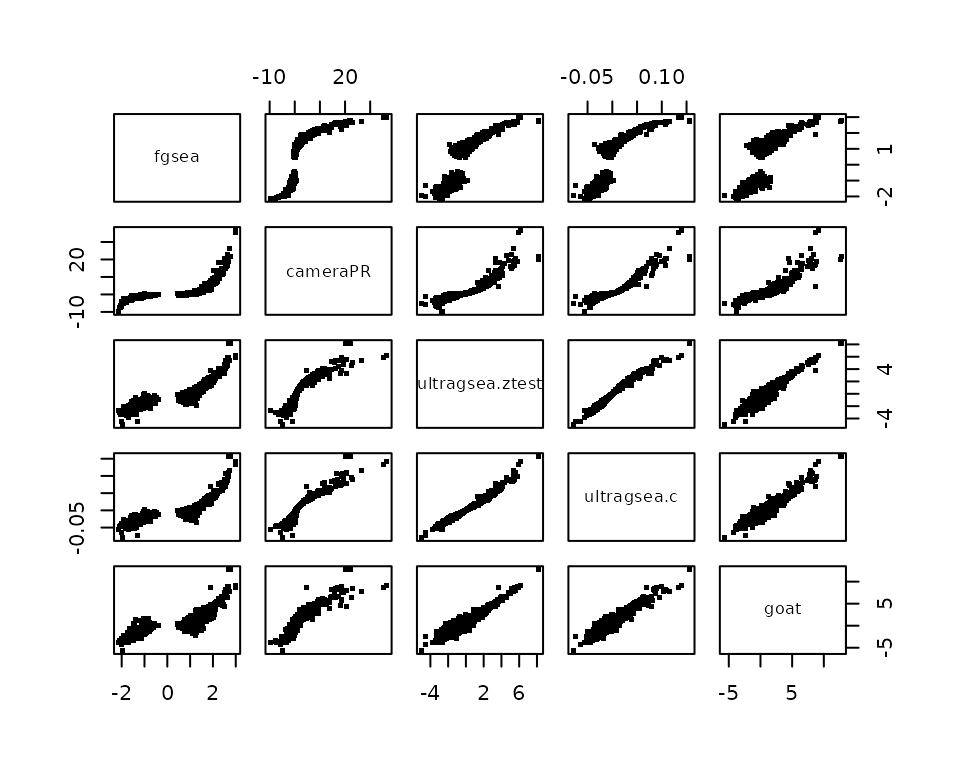
Notice the gap and the particular S-curve that fgsea shows. Also cameraPR shows some curve compared to the others. We can compare them better by comparing the ranks of the scores:

Comparing the p-values
Next, we can compare the p-values between the methods. Also here, we see that all p-values are highly correlated to each other.
P <- cbind(
fgsea = res.fgsea$pval,
cameraPR = res.cameraPR$PValue,
ultragsea.z = res.ultragsea.z$pval,
ultragsea.c = res.ultragsea.c$pval,
goat = res.goat$pval
)
mlp <- -log10(P)
pairs(mlp, pch='.',cex=4)
Replacing fgsea
Much of the slowness of fgsea can be attributed to the permutations for calculating the p-values. In the previous section, we have seen that the p-values from ultragsea (both cor and z-test) follow quite well those of fgsea. Therefore, to make fgsea::fgsea() faster, we can instead calculate the p-values using ultragsea. We created a replacement function for ultragsea::fgsea() that is 8-10x faster that the original fgsea::fgsea()
system.time(res1 <- fgsea::fgsea(gmt, fc))
#> user system elapsed
#> 5.573 0.093 3.616
system.time(res2 <- ultragsea::fgsea(gmt, fc))
#> user system elapsed
#> 0.233 0.108 0.273